Arthritis is defined as inflammation of joints affecting millions of people worldwide. There are more than 100 types of arthritis but the most common ones are osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis and so on. Gout also belongs to the group of frequent forms of arthritis and throughout this article; you’re going to learn more about it. The best way to manage your health condition is by getting educated about its causes, symptoms, treatments, and so on.
What Is Gout? How Common Is This Form of Arthritis?
Gout is defined as a rheumatic disease resulting from deposition of uric acid crystals in tissues and fluids in a person’s body. It is a complicated health condition that can affect anyone. Gouty arthritis is quite common and affects about 3.9% or 8.3 million adults in the United States.
While other types of arthritis primarily develop in women, the prevalence of gout is higher in men. In fact, 5.9% or 6.1 million adult men in the US have gout while 2% or 2.2 million women are affected by this condition. According to the CDC, the prevalence of gout has increased by 1.2% over the last two decades. When it comes to incidence of gout among males, it is more prevalent among black men compared to white men. For example, the cumulative incidence of gout among black men is 10.9% while in white men it’s 5.8%.

What Causes Gout?
An excessive amount of uric acid or hyperuricemia in the blood is the primary cause of gout. What is uric acid? Uric acid is a substance formed when the body breaks down purines, which are found in some foods and in human cells.
Your blood transports uric acid to the kidneys, then the substance is eliminated through urine. That said, some people overproduce uric acid or they produce normal amounts but their kidneys don’t process it properly. As a result, uric acid keeps building up.
Although the underlying mechanism that leads to hyperuricemia is unknown, doctors and scientists speculate that heredity plays a major role as well as different lifestyle factors. Excessive amounts of uric acid lead to the formation of crystals that build up in a person’s joints. These crystals are needle-like and sharp and they usually form around the joint or surrounding tissue, thus causing inflammation, pain, and swelling.
Gout Risk Factors
Although everyone can develop gout, some people are at a higher risk. Factors that increase your risk of gout are:
- Age and sex – as you already know men are more likely to develop gout than women. Regardless of the gender differences, the risk increases with age. One study found that in postmenopausal years, the gender difference between the formation of gout in men and women decreases significantly.
- Diet – generally, eating a diet that is high in seafood and meat, consumption of sweetened beverages with fructose, drinking alcohol, also increase one’s risk of gout
- Family history – just like with a wide array of health conditions, family history plays a major role
- Medical conditions – untreated hypertension and chronic conditions like diabetes, metabolic syndrome, and heart and kidney disease also make it more likely that a person will develop gout. Even some medications could increase your odds of getting this joint problem
- Overweight/obesity – people who are overweight or obese tend to produce higher levels of uric acid and their kidneys find it more difficult to eliminate it
- Recent surgery or trauma – recent surgery or trauma are also associated with higher risk of gout

Symptoms of Gout
Generally, symptoms of gouty arthritis occur suddenly, out of the blue, and in most cases, it happens at night without any warning whatsoever. In most cases, symptoms of gout include:
- Intense joint pain particularly within the first 4-12 hours after the gout attack begins
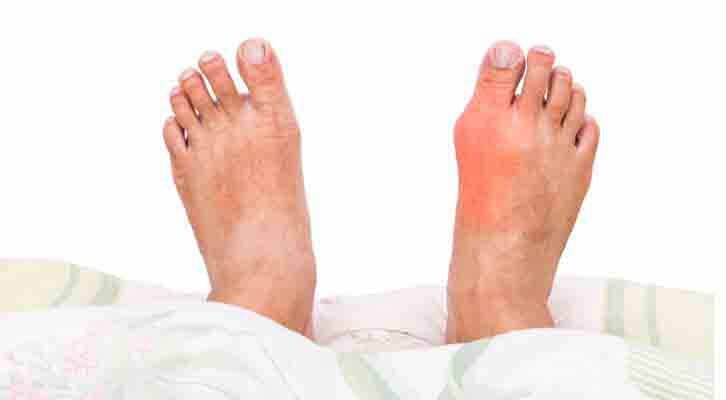
- Large joint of big toe is usually affected by gout the most, but it can develop in other joints too such as feet, ankles, knees, hands, and wrists
- Limited flexibility and range of motion
- Peeling, itchy, flaky skin as the swelling goes down
- Prolonged discomfort after the pain goes away; you may experience joint discomfort during the next few days or weeks. Later gout attacks may last longer, affect more joints, and lead to a greater joint discomfort
- The affected joints become red, swollen, warm, and tender
- The joint feels hot and very tender to the point that you can’t stand anything touching it, not even a blanket or bed sheet
How Is Gout Diagnosed?
It is highly important to see your doctor if you experience these symptoms because gout attacks become more frequent if the problem is left untreated. Based on the symptoms you describe and physical exam, the doctor will probably presume you have gout but he or she will also ask you about medical history, family history, diet, the severity and frequency of the attack, as well as what medications you’re using. To make the accurate diagnosis, your doctor will order some tests. Most common tests performed for gout diagnosis (and to rule out other problems) are:
- Blood test
- Dual energy CT scan
- Joint fluid test
- Ultrasound
- X-ray

Also Read – Parasites and Joint Pain Connection to Gout
How Is Gout Treated?
The primary goal of treatment of gouty arthritis is to provide pain relief and prevent future gout attacks as well as complications such as kidney damage or joint destruction. The treatment usually revolves around taking medications and making certain lifestyle changes. More specific treatment depends on whether a patient has acute or long-term gout.
The treatment plan for acute attack involves intake of medications such as NSAIDs (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs), colchicines, oral corticosteroids and you also have to rest the affected joint or more of them.
On the other hand, to manage long-term gout and prevent future attacks the doctor usually recommends medications like uricosuric agents, xanthine oxidase inhibitors, colchicines, pegloticase (Krystexxa). In cases when drugs and lifestyle modifications don’t help, the doctor may recommend surgery to remove large tophi (chalky nodules that form from uric acid crystals) that are causing deformity.
Lifestyle modifications that an affected individual can make to prevent gout attacks and improve the quality of life are:
- Reduce or avoid alcohol intake
- Lose weight
- Exercise regularly, you can ask your doctor or a fitness trainer to suggest some exercises if you’re not sure what to do
- Limit or avoid intake of beverages sweetened with fructose
- Drink plenty of water
- Limit consumption of foods high in purines.
Conclusion
Gout is a form of arthritis that primarily affects men, but women can develop it as well. Gout attacks are indicated by severe pain, tenderness, and swelling. It is recommended to see your doctor if you experience symptoms mentioned above. Prompt diagnosis and treatment can improve your quality of life and prevent future gout attacks.
You May Also Like – Can Alcohol Affect Arthritis Joint Pain?





 This article changed my life!
This article changed my life! This article was informative.
This article was informative. I have a medical question.
I have a medical question.
 This article contains incorrect information.
This article contains incorrect information. This article doesn’t have the information I’m looking for.
This article doesn’t have the information I’m looking for.